DESCRIPTION
Hysol® FP4322 is a high purity liquid epoxy encapsulant designed for semiconductor encapsulation. It is a high flow material which requires a cavity or flow control barrier to prevent excessive flow. Hysol FP4322 is suitable for encapsulation of bare chips mounted to plastic substrates as well as potting of small hybrid circuit modules. Spot encapsulation of bare chips on ceramic substrates is not suggested in most cases.
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
Semiconductor encapsulation.
PROPERTIES OF UNCURED MATERIAL
Color Black
Filler Content, % (ASTM D2584) 65
Specific Gravity @25°C, (77°F)
(ASTM D1475) 1.69
Shelf Life @-40°C (-40°F), months 9
Typical Value
Viscosity @ 25°C, (77°F)
(ITM2A) (ASTM D2393)
Brookfield RVF
Spindle 7, Speed 2, Cp 92,500
Spindle 7, Speed 20, Cp 52,500
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES, CURED MATERIAL
Color Black
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, in/in/°C
(ASTM D3386)
(40°-120°C) 30 x 10-6
Linear Shrinkage, %(ASTM D2566) .43
Density, gm/cc (ASTM D792) 1.7
Glass Transition, (Tg), °C, (ASTM D3386) 160
Hardness, Shore D (ASTM D2240) 97
Moisture Absorption, % (ASTM D570)
Immersion @ 100°C, 8 hrs 0.25
Extractable Ionic Content (ITM107B)
Chloride (Cl-), ppm 25
Potassium (K+), ppm 25
Sodium 25
Cured Electrical Properties
25°C
K D
1kHz 3.18 0.005
10kHz 3.15 0.006
100kHz 3.04 0.11
Volume Resistivity 6.2 x 1014
Surface Resistivity 1.6 x 1014
K = Dielectric constant by ASTM D150
D = Dissipation Factor by ASTM D150
Vol. Res.= Volume Resistivity in ohm-cm by ASTM D257
Surf.Res.= Surface Resistivity in ohm by ASTM D257
Handling
Pot Life @ 25°C, 77°F, days, 1
(ITM10T), time to double in viscosity
Gel Time @ 121°C, (250°F), minutes,
(ITM10N) 11
Shelf life at room temperature is approximately 2 days. Product may be stored at –40°C for greater than 6 months. Frozen packages must be thawed before use. Warm at room temperature until no longer cool to the touch (normally 20-60 minutes). Do not thaw in an oven or water bath. For best results FP4322 should be dispensed onto a substrate warmed to approximately 90°C. This will help minimize air entrapment under bonding wire.
GENERAL INFORMATION
For safe handling information on this product, consult the Material Safety Data Sheet, (MSDS).
This product is not recommended for use in pure oxygen and/or oxygen rich systems and should not be selected as a sealant for chlorine or their strong oxidizing materials
Cure Schedule
Recommended Cure 2-3 hours @ 170°C or
3-6 hours @ 150°C
Alternate Cure 1 hour @ 125°C plus
(Low Stress) 4 hours @ 150°C
(Designed for packages which are effected by high levels of stress.)
A two-step cure will minimize stress and warpage on large substrates. Curing below 140°C is not recommended. User should gel devices immediately after dispensing to prevent moisture degradation of ultimate cure properties. Use suggested cure schedules as general guidelines; other cure schedules may yield satisfactory results.
Note
The data contained herein are furnished for information only and are believed to be reliable. We cannot assume responsibility for the results obtained by others over whose methods we have no control. It is the user’s responsibility to determine suitability for the user’s purpose of any production methods mentioned herein and to adopt such precautions as may be advisable for the protection of property and of persons against any hazards that may be involved in the handling and use thereof. In light of the foregoing, Loctite Corporation specifically disclaims all warranties expressed or implied, including warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose, arising from sale or use of Loctite Corporation’s products. Loctite Corporation specifically disclaims any liability for consequential or incidental damages of any kind, including lost profits. The discussion herein of various processes or compositions is not to be interpreted as representation that they are free from domination of patents owned by others or as a license under any Loctite Corporation patents that may cover such processes or compositions. We recommend that each prospective user test his proposed application before repetitive use, using this data as a guide. This product may be covered by one or more United States or foreign patents or patent applications.
华为网盘下载:http://dl.dbank.com/c0akjfw9b5
点击下载附件:
 Henkel Loctite Hysol FP4322 TDS (22.7 KB, 154 次)
Henkel Loctite Hysol FP4322 TDS (22.7 KB, 154 次)


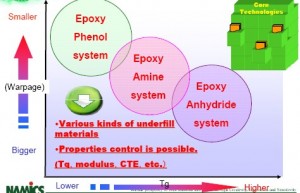
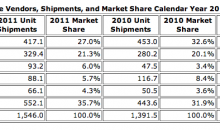
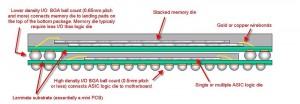








 汉高电子用胶彩页 (4.7 MB, 49 次)
汉高电子用胶彩页 (4.7 MB, 49 次)


《【扒一扒】日本高纯球形硅微粉材料生产商》: 作为一种无机非金属矿物功能性粉体材料,硅微粉广泛应用于电子材料、电工绝缘材料、胶黏剂、特种陶瓷、精密铸造、油漆涂料、油墨、硅橡胶等领域。 目前,世界上只有中国、日本、韩国、美国等少数国家具备硅微粉生产能力... 全文 ?